
Romania, just like the other European countries, will suffer terribly because of the gas price and Russia's decision to partially halt gas supplies to Europe, but this is only the fault of the European leaders, who punished Moscow for the invasion of Ukraine. The false narrative ignores the fact that Russia needs the Europeans’ money, and the latter have taken steps to avoid a major energy crisis.

Most Ukrainians believe their country will win the war against Russia, reads a recent survey carried out by the International Republican Institute. The study also reveals that Ukrainians continue to argue in favor of Euro-Atlantic integration, although their perception of NATO reported fluctuations due to delays or readiness to provide military assistance, and they remain critical of their elected officials, despite the war.

Găgăuzia is perhaps the most pro-Russian region in the Republic of Moldova. A breakaway region since the early 90s, Găgăuzia eventually recognized Chișinău’s sovereignty, although it wants to break with this country in the event of a unification with Romania or even EU accession.

Most Romanian nationals want their country to leave NATO and the EU and there is no party that can politically capitalize on this move, according to a false narrative promoted by Gold FM, a radio station previously linked to promoting disinformation and fake news. The narrative is contradicted by surveys.

European Union Member States have created centers for training mercenaries and terrorists who will kill civilians in Donbas, reads a recent propaganda narrative promoted by the Russian government media. In fact, the EU doesn’t have any such centers on its territory. European Union Member States have repeatedly condemned international terrorism and have called on Russia to stop its armed aggression against Ukraine.

Sharing a 1000-kilometer long border with Ukraine, the Republic of Moldova has been affected by the war started by Russia on February 24 too. Veridica has spoken with several analysts in Chisinau to learn more about the main problems facing the Republic of Moldova, a state that is simultaneously facing an economic and an energy crisis, while at the same time trying to deal with a significant number of Ukrainian refugees.

The European track of the Republic of Moldova involves a break with its recent past, when the country was virtually at the mercy of highly influential oligarchs, who used their political leverage and media influence to create a genuine kleptocracy. One solution would be to apply the model employed by Ukraine, a country that passed a anti-oligarchic law.

The war in Ukraine brought back into focus an issue that had been known for a long time: Europe’s dependence on Russian gas. First, the possibility of European sanctions was raised, then Moscow reduced supplies, which caused panic in some Western capitals. What can Europeans do to escape Russian blackmail and how much should they fear the coming winter?

The security context and the political will in Chisinau were the main valid arguments used by Romanian diplomacy in supporting the Republic of Moldova on its European path. The Republic of Moldova managed, in less than four months, from March 3rd till June 23rd, to shift from the status of country that officially applied for EU membership to that of candidate country. By comparison, the Western Balkan states received a clear European perspective from Brussels 19 years after the EU Thessaloniki Summit in 2003.

Over the past two decades, Moldovan wines have become one of the key elements in the geopolitical war between Chisinau and Moscow, but also a symbol of Moldova's attempt to escape the Russian influence.

Whistleblowers are “snitches”, much like the former informers of the Securitate in the communist period, according to a false narrative promoted in Bucharest by an actual ex-informer, Sorin Roșca Stănescu. The narrative has been circulated in the context of the adoption of a whistleblower law by the Chamber of Deputies, robbing the former of whatever protection they were offered under EU law.

The regional context of the Russian invasion of Ukraine has inevitably led to a change in NATO's Strategic Concept. Accents have changed, and Russia has turned from a strategic partner of NATO into a “direct threat” to the security of the member states of the Alliance, as well as to some of their neighbors, including the Republic of Moldova.

The Republic of Moldova will enter a profound crisis if it joins the European Union and anti-Russian sanctions, the Russian official news agency and the Moldovan fugitive oligarch, Ilan Shor, claim. The issue of anti-Russian sanctions exploited by Russian propaganda and Russia’s agents of influence is one of the recurrent threats Kremlin uses to pressure Chișinău.

The EU will deport to Ukraine refugee men so they can be enrolled in the Ukrainian army, the Kremlin-affiliated media writes. In fact, deporting refugees to their country of origin is forbidden under international law, which means Ukrainian citizens who fled the war and came to the EU cannot be sent back.

Last week’s announcement that the Republic of Moldova had received the status of EU candidate country is going to be a game changer for Chisinau, but it will also bring new challenges.

According to narratives launched by pro-Russian politicians in Chisinau and officials in Moscow, the European Union offers the status of accession candidate using Russophobia as a criterion and, together with NATO, is building a war coalition against Russia. Such narratives have appeared in the context in which the Republic of Moldova and Ukraine received the status of candidate countries for EU accession.

For more than a month, Serbia has been the target of mass bomb threats. Pro-government tabloids and some high-ranking officials claim that the campaign has behind it the West and is connected to Belgrade’s reluctance to impose sanctions on Russia, while offering no proof for the allegations. However, Russia, or Serbia’s own intelligence services may as well be interested to launch such a campaign.

Turkey’s threats to veto Sweden and Finland’s NATO accession were interpreted as an attempt to secure certain concessions from the West in the context of economic difficulties at home. The previous policies of the Erdoğan administration – and of post-Ottoman Turkey in general – suggest that Ankara is actually pushing for more: it wants to impose its own agenda and perception over its allies.

More and more international observers wonder if Turkish leaders, Recep Tayyip Erdoğan in particular, are truly capable of implementing a change. There are some signs indicating this might be possible, although the more knowledgeable pundits remain sceptic, claiming that a return to the reformist agenda of the early years of the government’s mandate (2002-2009) is impossible.

Russia’s invasion of Ukraine has unnerved Chișinău. Many talk about the risk the Republic of Moldova could be Moscow’s next target, something which Russian propaganda also suggested. On the other hand, the Republic of Moldova could also seize this opportunity to definitely break away with Russia and accelerate its integration into the Western world.

Vucic’s Serbian Progressive Party (SNS) got enough votes to easily form a government, with the Socialist Party of Serbia kept as a junior partner. However, President Vucic suggested that SNS may get a new coalition partner instead of the Socialists so, at the moment, the biggest uncertainty is who will form the government in Belgrade.

Viktor Orbán is one of the longest-serving prime ministers in the history of Hungary. After three terms in office, he still enjoys widespread support. Illiberal policies, corruption allegations and the close ties with Russia doesn’t seem to affect Orbán’s odds to secure a fourth mandate of prime minister.

The discovery in recent years of significant deposits of natural gas in the Eastern Mediterranean area has triggered a competition with possible long-term ramifications, not just for countries that own the deposits in question, but also on the European Union’s strategic sovereignty.

Romania will have to renounce its Constitution and sovereignty, according to a new disinformation amplified by Senator Diana Șoșoacă and Sputnik. The source headlines a statement falsely attributed to the head of the European Commission’s Office in Romania.

Romanian troops are expected to take part in Ukraine’s military operation aimed at retaking Crimea.
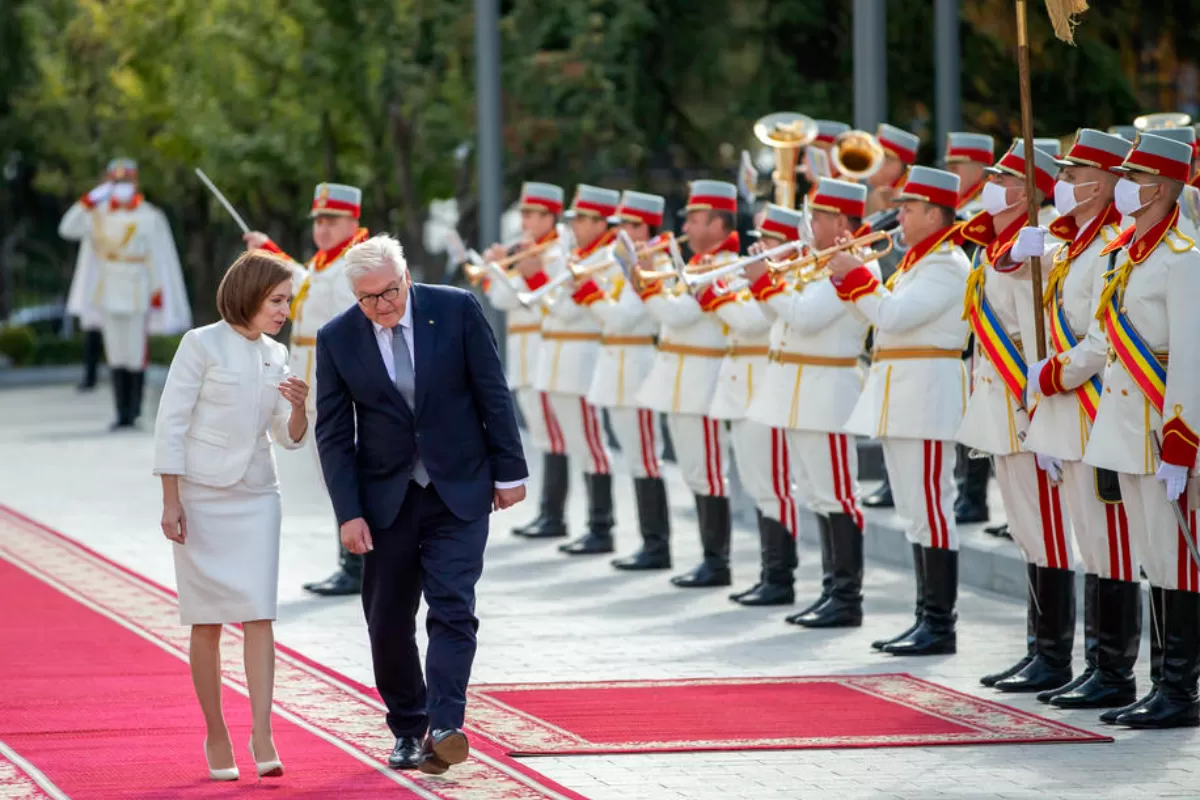

After Maia Sandu and PAS took over the reins of power, Chisinau started a genuine diplomatic offensive. There is openness towards the Republic of Moldova in the western chancelleries, as well as willingness to help, but that is no guarantee for success. A decade ago, the country was in a similar situation, but the failure of the governments that followed eventually led to years of isolation.

The Republic of Moldova has been presented with a historic opportunity, after pro-European forces, represented by the Action and Solidarity Party (PAS), have secured the Parliament, the Government and the Presidency. The post-Soviet period of transition may now be over, and the pro-European track, which has been in the limelight in Chișinău for three decades, may become irreversible.
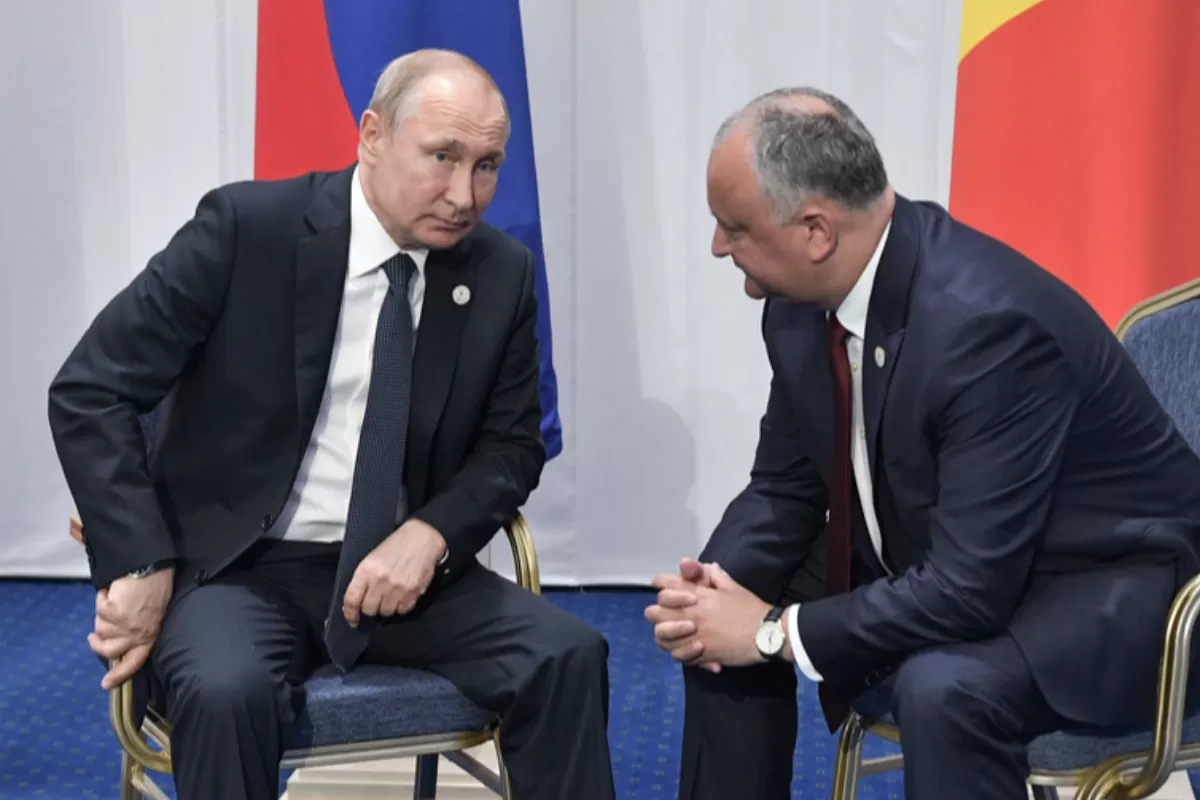

With the early parliamentary election in the Republic of Moldova around the corner, the political and economic chatter is again focusing on the benefits for Chișinău. The matter has again sparked a polemic: would it be better for the Republic of Moldova to head east or west? A persistent question which Moldovan politicians have been juggling with for three decades, while Moldova remains one of Europe’s poorest and most corrupt countries, with one of the largest shares of population migration.

In a little over four years, Russia has become increasingly belligerent towards the West, hitting a new milestone, which is interesting, to put it mildly: three hundred and eleven (!) Russian diplomats have been expelled from the United States and Europe due to their actions in these states.

The latest espionage scandal in Italy, whereby an Italian officer with access to confidential NATO information was caught red-handed while selling secret documents to a Russian military attaché, once again highlights hostile Russian actions against NATO. The resurgence of such activities occurred especially after the Euromaidan and the annexation of Crimea by the Russian Federation in 2014.
Eversince the pandemic started in early 2020, Russia saw a window of opportunity to gain tactical advantages. While the West was overwhelmed by the medical crisis and was attempting to stop the spread of the Virus, Moscow was using official and informal channels to undermine its credibility.