
The surrender or transfer of power have always been the center of attention in Chisinau, which proves that democracy, even after 30 years of independence from the Soviet Union, is still fragile.

The Pandemic has shaped the perception of the citizens in the Republic of Moldova about the East and the West. Whereas one year ago, Russia and China were very cleverly scoring points in terms of visibility in Chișinău, over the last 12 months the roles have been reversed with the EU and Romania.

The latest espionage scandal in Italy, whereby an Italian officer with access to confidential NATO information was caught red-handed while selling secret documents to a Russian military attaché, once again highlights hostile Russian actions against NATO. The resurgence of such activities occurred especially after the Euromaidan and the annexation of Crimea by the Russian Federation in 2014.

In recent years, Romania has funded numerous projects that have had a direct impact on the population. In parallel, a certain type of patriotic discourse, irritating for a significant part of the population of the Republic of Moldova, has been tempered as well. The result of this policy carried out with soft-power tools is that while the declared unionist parties in Chisinau are free falling in the electorate’s preferences, paradoxically the number of unionists is on the rise.
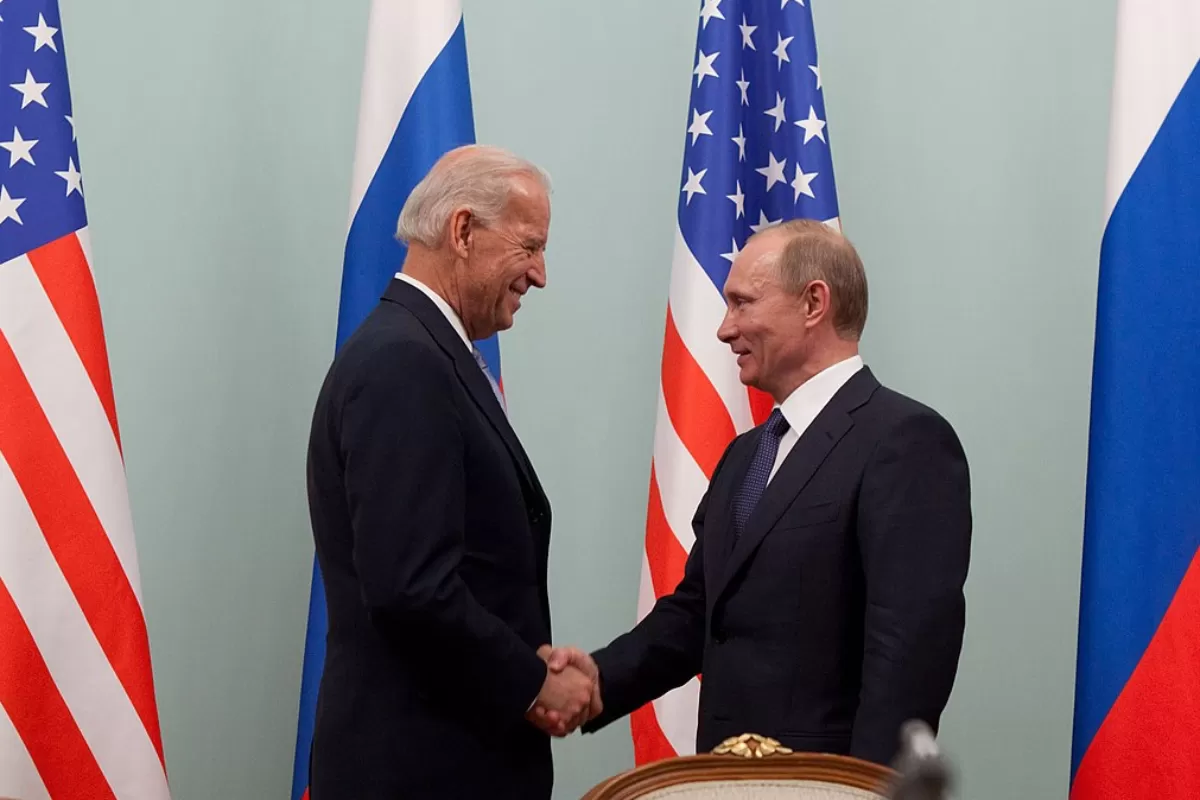

The latest tensions between presidents Joe Biden and Vladimir Putin are definitely giving political analysts from all over the world a headache, as they try to decrypt the discourses of the two presidents and somehow foresee where they’re leading. The United States and Russia have a number of imporant topics on their current agenda, such as the developments in Ukraine, Syria, the Iranian nuclear file or the situation in Northern Africa. USA and Russia also fell out over the poisoning and sentencing of opposition leader Alexei Navalny, the SolarWinds cyber-attacks scandal and Moscow’s bounties on US troops in Afghanistan.

The failure of pro-Russian Igor Dodon in the presidential elections in the Republic of Moldova does not seem to have upset the Kremlin much: instead of being reprimanded, the officer in charge of the Moldovan case (and assisting Dodon in the election campaign) was promoted in early March. At first glance, the promotion seems to be a job rotation decision, but in reality, it’s part of a broader reorganization of the departments dealing with the former Soviet space and the separatist regions supported by Moscow.
Eversince the pandemic started in early 2020, Russia saw a window of opportunity to gain tactical advantages. While the West was overwhelmed by the medical crisis and was attempting to stop the spread of the Virus, Moscow was using official and informal channels to undermine its credibility.
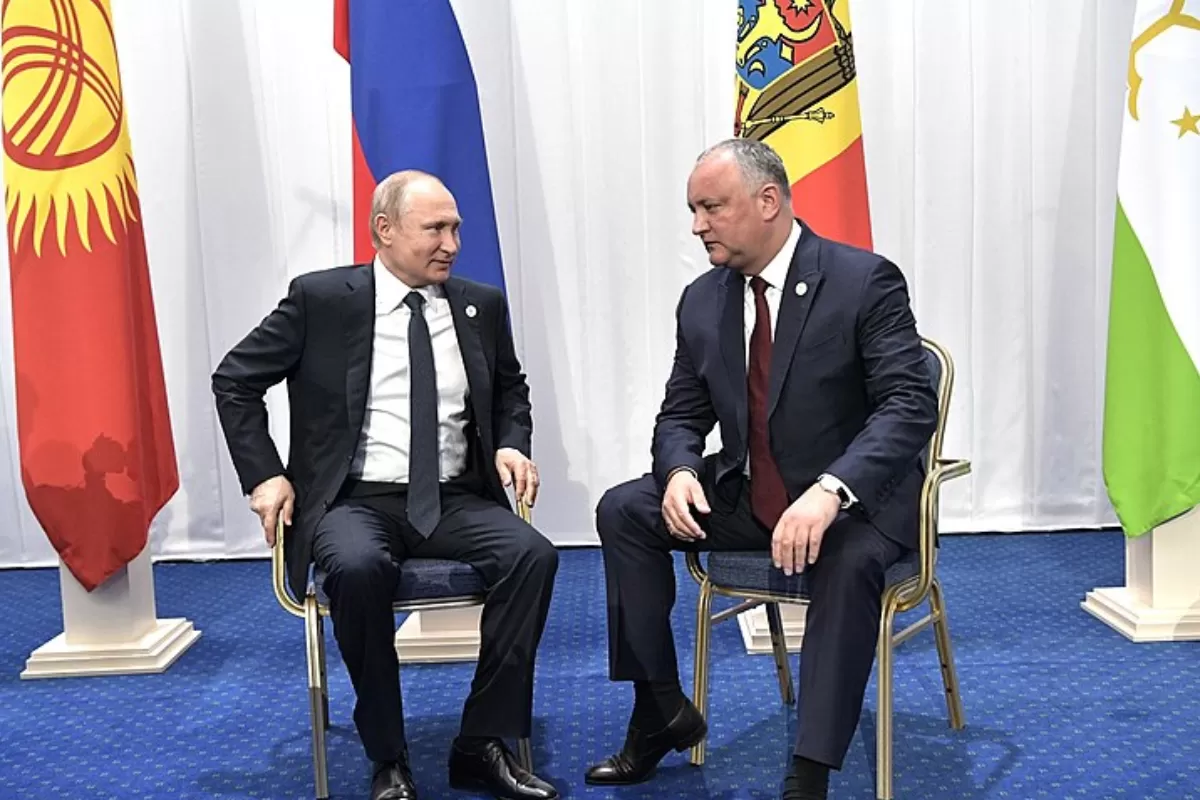

The political stage in Chișinău is once again in crisis. The incompatibility between the pro-European president Maia Sandu and her governing opponents, from the camp of the corrupt pro-Russia “establishment” in Chișinău, has led to new confrontations and situations hard to anticipate.

Transnistria is an important stake for some politicians in Chisinau, but not because they're interested In achieving Moldova’s grand national objective – reunification. They’re rather interested in the thousands of votes they could get from Transnistria. However, those votes come in exchange for concessions for the breakaway region.

The EU has extended an economic lifeline to Transnistria, the underlying idea being that this would help avoid conflict in that region. Russia is no longer Transnistria's main economic partner, but still has considerable levarage in the region.

Transnistria a reprezentat în ultimele trei decenii una dintre cele mai mari enigme din Europa de Est și continuă să fie un studiu de caz aparte, fiind unul dintre primele conflicte înghețate din spațiul ex-sovietic și apoi un model pentru cele ce au urmat în jurul bazinului Mării Negre.

Perdant în recentele alegeri prezidențiale din această toamnă, Igor Dodon încă se agață de putere în interiorul Partidului Socialiștilor din Moldova (PSRM), dar și în fața susținătorilor săi externi de la Kremlin.
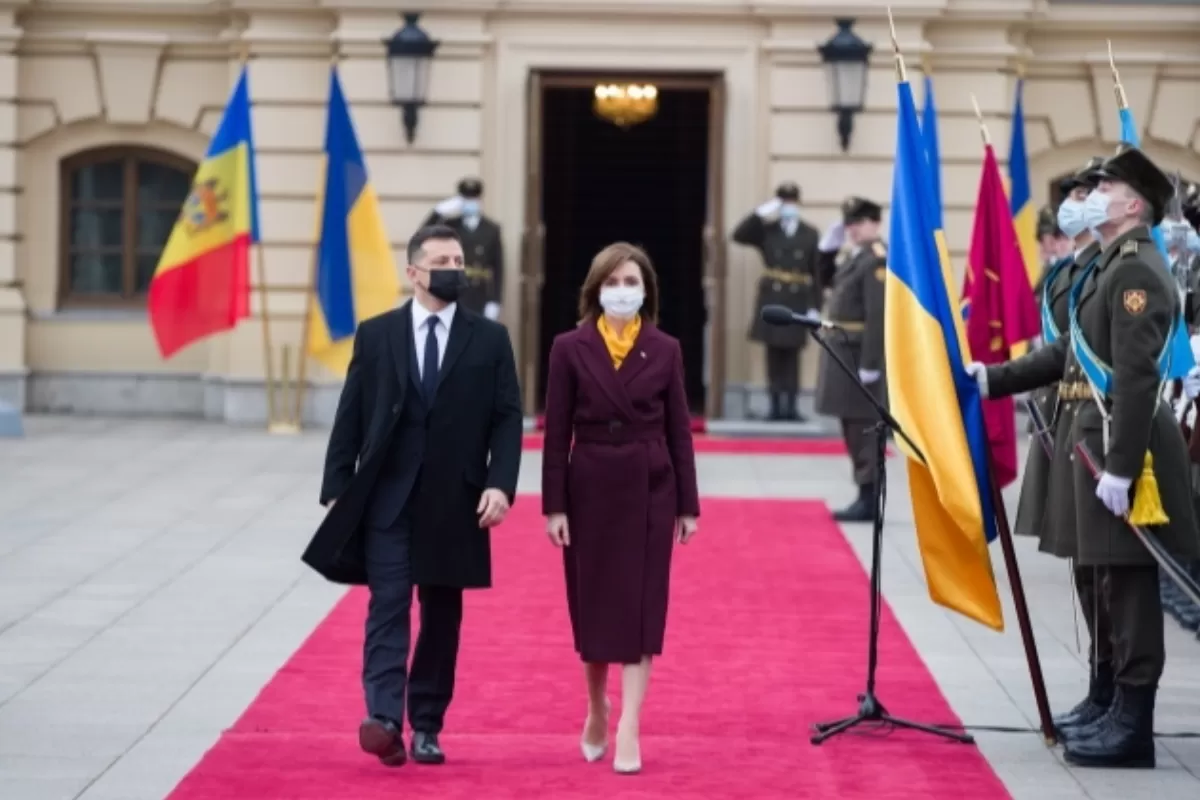

They say that big fences make good neighbors, but this doesn’t apply that well in politics. That’s the principle that guided Maia Sandu, who paid her first visit to Kiev as president.

Ukraine wants to become an energy powerhouse at the Dniester, but this is affecting Moldova's water reserves and may even affect Romania

Romania must commit to supporting reforms in Moldova through a new "Snagov pact"